Integer Types
Integer Types: Definition, and Advanced Calculations
Integers form the foundation of calculation in maths. Whether we are solving simple arithmetic problems, working with algebraic expressions, performing integer arithmetic in computer architecture, or developing advanced calculators, integers play a critical role.
They represent whole numbers without fractional or decimal parts, making them ideal for clear, precise, and error-free calculations. In this article, we will explore the definition of integers, important integer types, their usage in modern mathhttps://www.calculator-org.com/category/mathematical-terminology/ematics, and how they power advanced online calculators
Are Integers whole numbers?
Yes, Integer whole numbers can be positive, negative, integer 0. Unlike decimals and fractions, integers do not contain fractional parts. This makes them simple yet powerful, widely used in arithmetic, , number theory, and computational systems.
Integer and Whole Number
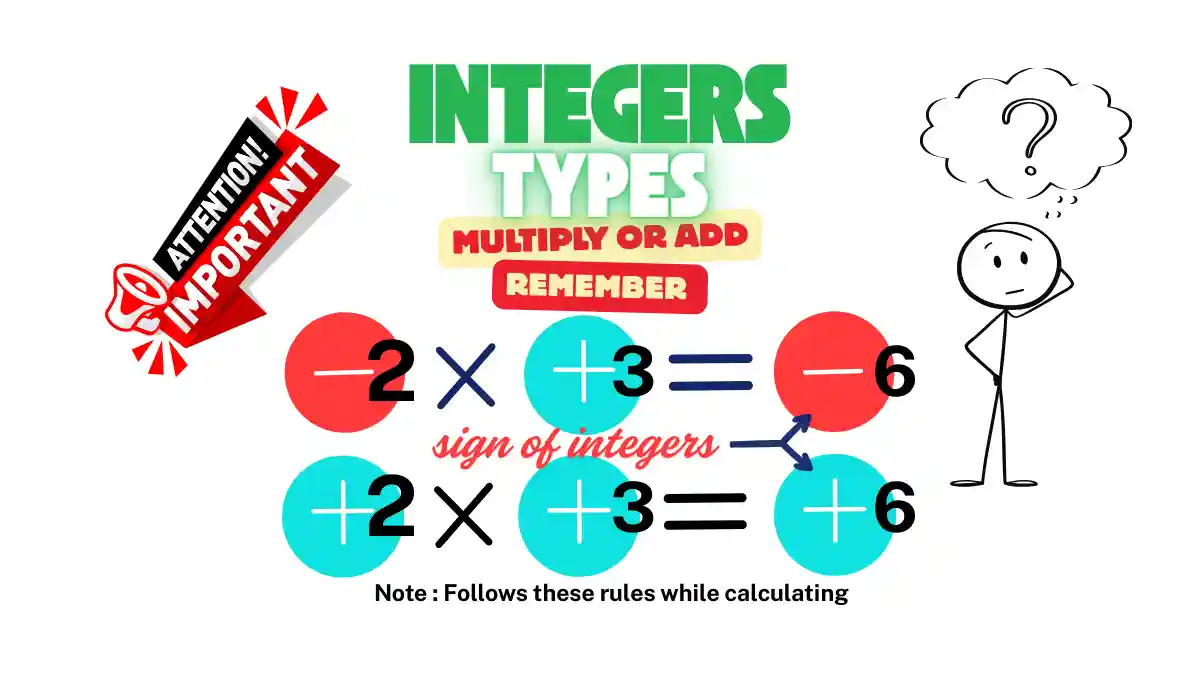
An integer includes all +ve numbers, -ve numbers, and zero, while a whole number includes only zero and +ve numbers. This means all whole numbers are integers, but negative integers are not whole numbers. they extend in both directions on the number line, making them more useful for showing loss, direction, and temperature changes. We hear temperature drops to -10C and such examples in our routine life
Integer Value Examples:
-5, -4, -3, -2, -1,0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6
Integers are represented on a number line extending infinitely in both directions. Zero stands at the center, positive integers lie to the right, and negative integers lie to the left. Their ability to describe increases and decreases, gains and losses, and directional changes makes them highly practical in real-life situations and computer-based applications.
Integer Types
Although integer types appear simple, they can be divided into several important categories. Understanding these integer types helps learners and calculator users perform more precise operations.
1. Positive Integer Types:
These are whole numbers greater than zero. They represent quantities, counts, and natural numbers used in daily life. An integer data type example for whole numbers includes 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 and so on; it stores whole values without decimals, making it suitable for counting, indexing, and simple arithmetic operations.
2. Negative Integers 5 Examples
Numbers less than zero are classified as negative integers. They are used to show decreases, deficits, or positions below a baseline.eg −1, −3, -5, −7, -8
3. Integer of zero
An integer of 0 is a whole number that represents neither positive nor negative. 0 integer acts as the neutral element in addition and subtraction, serves as a starting point on the number line, and is essential in counting, calculations, and programming.
4. Even Integers
Even integers are divisible by 2 without a remainder.
Examples: −8, −2, 0, 4, 10
5. Odd Integers
Odd integers are not divisible by 2 and always leave a remainder of 1 when divided by 2.
Examples: −5, −3, 1, 9
6. Prime Integers (Prime Numbers)
These are positive integers greater than 1 that have exactly two factors: 1 and themselves.
Examples: 2, 3, 5, 11, 17
7. Composite Integers
Composite numbers are positive integers greater than 1 that have more than two factors.
Examples: 4, 6, 9, 12, 20
Conclusion
Integers in calculators and computers are stored and processed in binary. Converting an integer to binary allows accurate arithmetic operations, including addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. Using integer into binary, calculators and programs perform fast, precise, and error-free calculations, enabling efficient integer arithmetic internally while displaying decimal results to users.
Calculators use integer float types to handle numbers: integers for whole-number operations and floats for decimals. Internally processed in binary, integer float enables fast, precise calculations for counting, measurements, and fractional results efficiently.
Integers are fundamental to mathematics, technology, and daily life. From simple arithmetic to advanced number theory, integers help us measure, compare, and calculate accurately. Understanding the main integer types—positive, negative, zero, even, odd, prime, and composite—gives clarity to both learners and developers.
These types also empower online tools, making integer-based calculators fast, accurate, and easy to build. As digital learning grows, the role of integers in calculators and mathematical tools becomes even more important. Whether for algebra, programming, number theory, or real-life decisions, integers remain a cornerstone of modern calculations and problem-solving.