Pyramids
Mathematical Pyramids: Types, Formulas, and Their Importance
Pyramids are among the most fascinating geometric solids in mathematics. While inspired by the Egyptian pyramids, in mathematics a pyramid is defined as a solid with a polygonal base and triangular faces meeting at a single apex.
Mathematical pyramids are studied for their geometric properties, volume, surface area, and applications in both theoretical and practical fields.
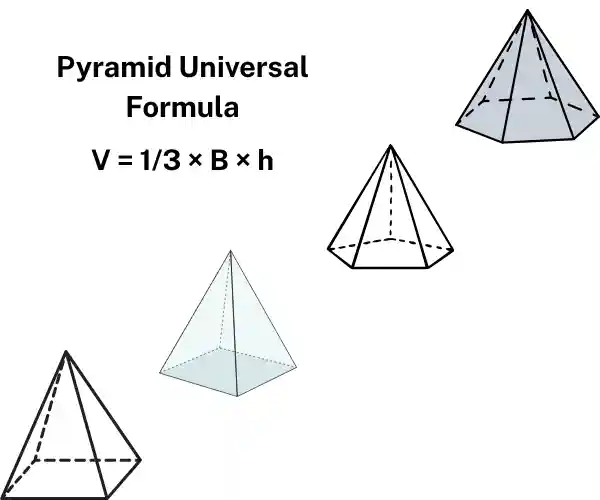
Definition of a Pyramid and volume of a pyramid formula
A regular pyramid is a 3D shape with a regular polygon base and triangular faces meeting at an apex. The volume of a regular pyramid is found using the formula: one-third × base area × height. Calculating pyramid volume is essential in mathematics, geometry, and architecture.
Using the volume of regular pyramid formula allows comparison with prisms and other solids. Understanding regular pyramid volume helps in measurement and spatial reasoning.
Tools and calculations make it easier to find the volume of regular pyramid for any regular polygon base, making real-world applications simple and precise. A pyramid is a solid with a polygonal base and triangular faces that meet at one apex. The universal formula for volume of pyramid is:
Where: V = Volume of pyramid
B = Area of base
h = Perpendicular height from base to apex
Note: This formula applies to all pyramids, no matter the shape of the base.
Types of Mathematical Pyramids
Pyramids are classified according to the shape of their base. Each type has specific Pyramid volume formula and pyramid surface area.
1. Square Pyramid
A square pyramid is a shape with a square on the bottom and four triangle sides that rise up and meet at one sharp point on top. It looks like a little mountain, a tent, or even a toy house roof. The square base keeps it flat and steady, while the triangles make it tall.
Inside the pyramid is empty space, called volume, which tells us how much the pyramid can hold. This simple shape helps children imagine how flat shapes can join to make solid 3D objects.
The volume of a pyramid with a square base tells us how much space is inside it. The pyramid has a square bottom and four triangle sides that meet at one point on top. Knowing its volume helps us understand how big the shape really is inside.
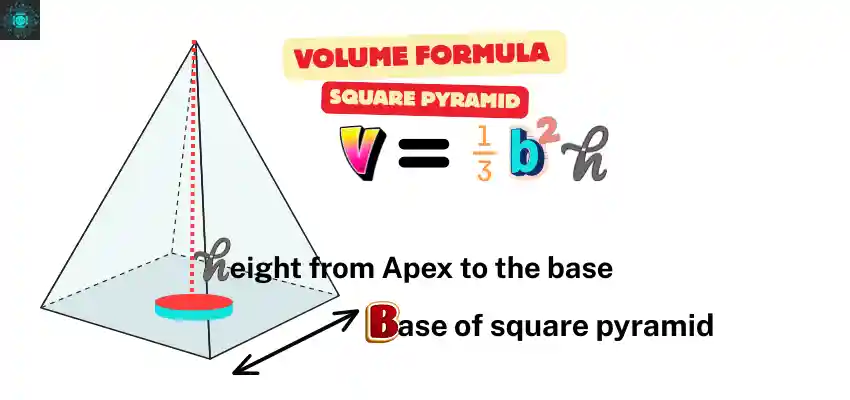
How to find the volume of a pyramid
The volume of pyramid with square base is found by first getting the area of its square bottom and then using the height. When we take one-third of the base area multiplied by the height, we get how much space the pyramid has inside.
Pyramid with a square base and four triangular faces.
Base Area: B = a × a
Where a = side length of the square
Pyramid Volume equation: V = 1/3 × a × a × h
Solved example
Lets find volume of a square pyramid with base 8m and heieht with 11m
Sol: We know
Note: Write answer in Square as cm2, mm2 in2
For a square pyramid, how calculate surface area means adding the area of its square base and the four triangular faces. First find the base area, then the area of each triangle, and add them all to get the total surface area.
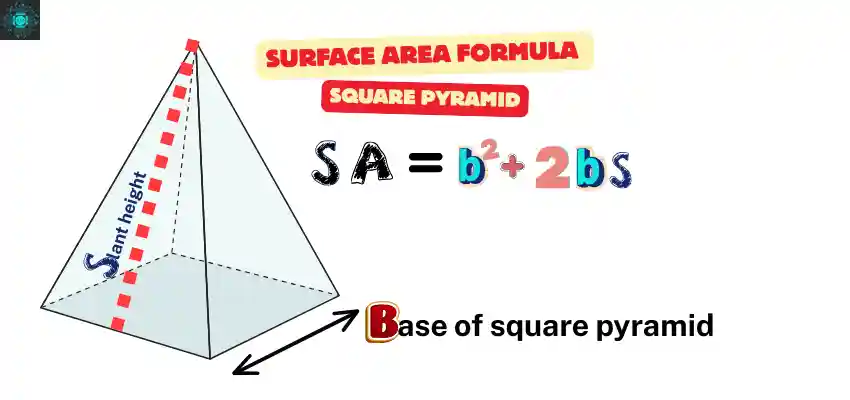
Surface Area of a pyramid:
S = Slant height
Where b= base
Example
Lets find out the lateral and total surface area for a square pyramid with bas of 8m and slant height of 14m;
Solution:
Sol; we know that
lateral surface area (LSA)=2bs
You know: b=9 and s=14
hence, putting value
LSA= 2*8*14
= 224m2
Now we can find total surface area with equation
TSA=b2+LSA
=82+224
=64+224
TSA=288m2
Significance: A square pyramid exists in real life, such as the famous Egyptian pyramids, and is an important shape in mathematics. It helps students understand geometry, surface area, volume, and how flat shapes come together to form solid structures
2. Rectangular Pyramid
A pyramid with a rectangular base is a geometric 3D shape with a rectangular bottom and triangular faces meeting at a single apex. It is widely studied in mathematics for its properties and real-world applications.
To find its volume, use the formula: one-third × base area × height. Similarly, knowing how to find volume of a rectangular prism is important for comparison and calculations. Tools like a rectangular tank volume calculator help in practical scenarios.
Studying the volume of pyramid with rectangular base and rectangular prisms aids in understanding geometry, measurement, and spatial reasoning.
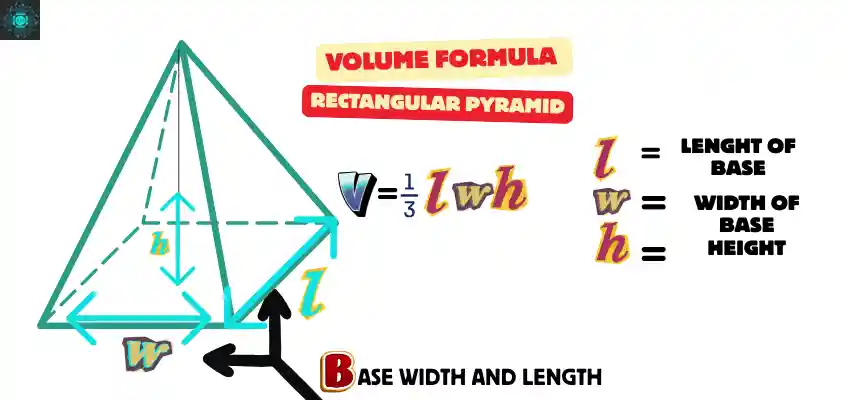
Pyramid with a rectangular base.
Base Area:
B = l × w
Where l = length, w = width
How to find volume of a pyramid for rectangular shape
Example
let’s find volume of rectangular pyramid with base length l=16m, base width b=10m and height =25.
$$V = \frac{1}{3} \cdot l \cdot w \cdot h$$
Step 2: Substituting values:
$$V = \frac{1}{3} \cdot 16 \cdot 10 \cdot 25$$
Step 3: Multiply numerator:
$$V = \frac{4000}{3}$$
Step 4: Final result:
$$V \approx 1333.33 \, m^2$$
How to find surface are of a rectanuglar Pyramid
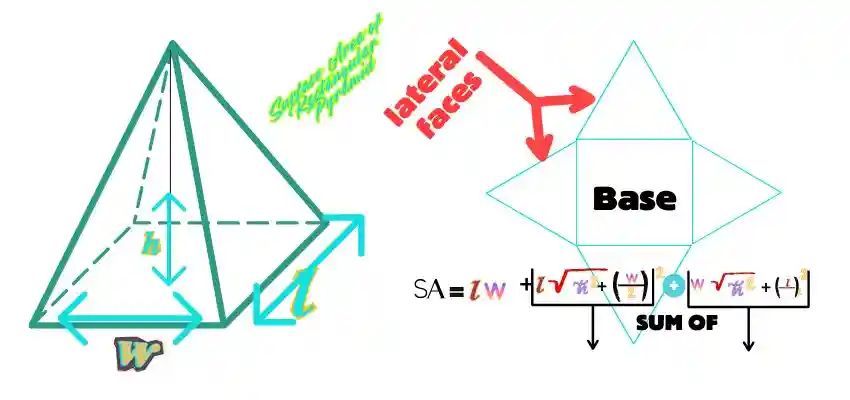
Surface Area of pyramid:
How to find surface area of rectanuglar pyramid
Surface area is defined as region occupied by its surfacces and is measured in units in square as cm2,in2 m2and so on Rectanuglar pyramid has two surface areas, TSA AND LSA.
TSA stands for total area of surface and LSA stands for lateral triangular surfaces as show in above picture.
Lateral Surface Area
This is equal to the sum of all four lateral faces or say triangular faces wehere area of opposite triangular faces is identical, hence to find LSA, we require base lenght, and base width and slant height of triangular faces.
Therefore LSA = Sum of lateral triangular faces
Formula
As we know that Area of tringle=1/2 base×height
and Area of trinagular that has base length=1/2×l×{√h2+(l/2)2} and Area of triangular that has base width=1/2×w×{√h2+(w/2)2}
Now sum of all the four is equal to;
Total Surface Area
TSA is equal to sum of the areas of tis 4 lateral surfaces and area of its reactangular base, to find TSA we need area of its rectangular base and lateral surfaces eg sum of 4 triangular faces.
TSA= LSA +Area of base
here area of base is =lw
Significance: Rarely built in reality, mostly studied mathematically.
3. Triangular Pyramid
A triangular pyramid is a solid shape made of four triangular faces that meet at one point. These triangular pyramid faces form a closed 3D object with space inside it. To find the volume of a triangular pyramid, we calculate how much space the shape holds.
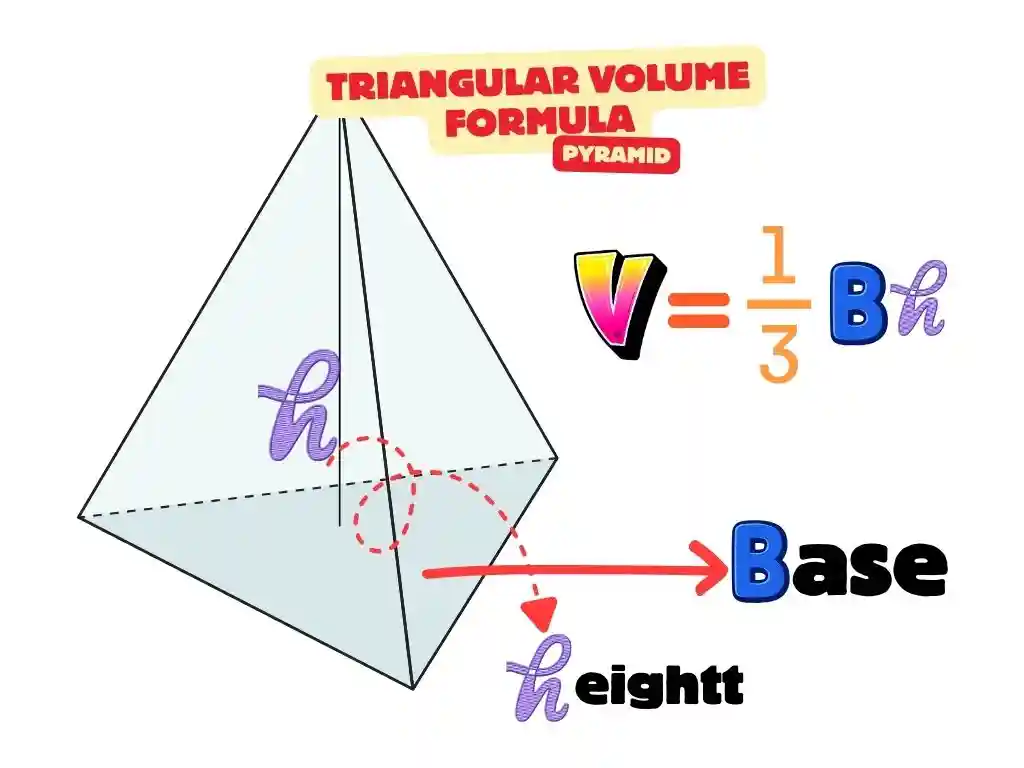
The rule for the volume of pyramid with triangular base is to take one-third of the area of its triangular base multiplied by its height. Tools like a volume of a triangular pyramid calculator or a volume calculator triangular prism help students check their answers and quickly measure total content inside similar shapes.
Pyramid with a triangular base.
Where b = base of triangle, h_base = height of triangle
How to find volume of pyramid
Solved example
Lets find volume of a triangular pyramid with base area of 75meter square and height from apex 25m. Solution;
Understanding how volume works in triangular pyramids makes it easier to study real structures, model objects, and compare different 3D shapes.
Formula for Volume of a pyramid:
V = 1/3 × B × h
How to find the surface area of a pyramid Triangular
Surface Area:
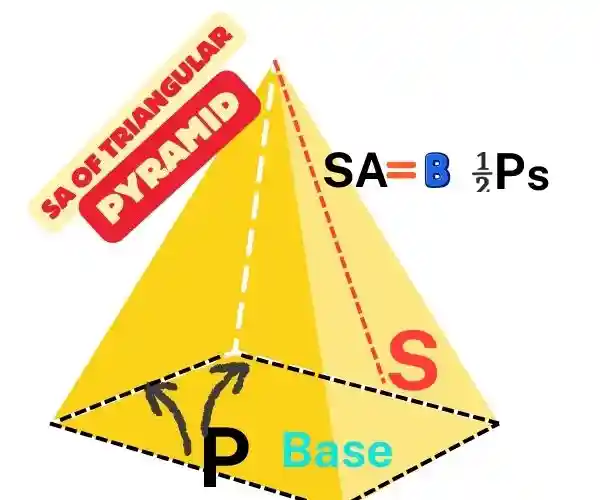
There are two formulas, the first one is if all the angles are of different, means the pyramid is irregular.
Where l1, l2, l3 = slant heights of triangular faces
and in case of regular triangular pyramid having all slant heights equal
Solved Example
lets find the surface area of regular triangular pyramid with base area of 86 meter square, a base perimeter of 60m, and slant height of 16m.Solution as follows;
Significance: Mostly theoretical, used in 3D modeling, chemistry, and mathematics.
4. Pentagonal or n-sided Pyramid
- Definition: Pyramid with a regular n-sided polygon as the base.
- Base Area (Regular Polygon):
Where a = side of polygon, n = number of sides
- Significance: Mainly theoretical; used in mathematics, computer graphics, and modeling.
Theoretical vs Real Pyramids
Mathematics allows pyramids with any polygonal base, but not all exist physically:
- Real pyramids: Square pyramids (Egyptian pyramids), some rectangular pyramids in modern architecture.
- Theoretical pyramids: Triangular, pentagonal, hexagonal, or n-sided pyramids are mainly studied mathematically.
Applications and Importance of Pyramid Formulas
- Education: Teaching volume, surface area, and 3D geometry.
- Engineering & Architecture: Calculating materials, structural loads, and stability.
- Digital Applications: CAD, 3D printing, and simulations use these formulas.
- Scientific Modeling: Molecular geometry, crystallography, and computational models rely on accurate pyramid formulas.
The universal formula:
V = 1/3 × B × h
works for all types of pyramids and is essential for theoretical and practical calculations.
Conclusion
Mathematical pyramids extend far beyond ancient monuments. Classified by base—square, rectangular, triangular, or n-sided—they are central to understanding volume and surface area in mathematics. While some pyramids exist physically, many are theoretical, studied for geometry, science, and modeling.
The study of pyramids demonstrates the universality of mathematics, bridging ancient architecture with modern engineering. Proper formulas allow precise calculations, making pyramids one of the most elegant and widely studied geometric solids.